Exploring Stablechain: Revolutionizing Stablecoin Transactions with a Dedicated Blockchain
By Micah Oguguo
The cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve at a breakneck pace, with stablecoins emerging as a cornerstone of the digital economy. Among the latest innovations making waves is Stablechain, a purpose-built Layer 1 blockchain designed to optimize transactions using Tether’s USDT, the world’s leading stablecoin with over $150 billion in circulation.
Introduced on July 1, 2025, via a detailed announcement on X by the @stable account, Stablechain promises to redefine how we interact with stablecoins, addressing longstanding inefficiencies in existing blockchain infrastructures.
This article delves into the concept of Stablechain, its technical underpinnings, potential implications, and the questions it raises about decentralization and scalability.
The Rise of Stablecoins and the Need for Stablechain
Stablecoins like USDT have transcended their initial niche as a hedge against cryptocurrency volatility, becoming a global financial tool. With 350 million users and transaction volumes surpassing Visa, USDT powers decentralized finance (DeFi), cross-border payments, and international commerce.
However, this rapid adoption has exposed the limitations of current blockchains—high fees, slow settlement times, and complex user experiences have hindered seamless integration into everyday use. Traditional blockchains, optimized for general-purpose applications, struggle to meet the specific demands of stablecoin transactions, which prioritize speed, low cost, and reliability.
Enter Stablechain, coined as the "first stablechain," a dedicated Layer 1 blockchain tailored for stablecoin operations. The project aims to bridge the gap between the agility of cryptocurrency and the stability of fiat, offering a scalable infrastructure that could transform global payments. By leveraging USDT as its native gas token and introducing gas-free peer-to-peer transfers, Stablechain seeks to eliminate the friction of holding volatile tokens for transaction fees—a bold departure from the norm.
Core Features and Technical Innovations
Stablechain’s design is a response to the inefficiencies plaguing existing systems. Here are its standout features:
USDT as Native Gas: Unlike Ethereum, where users must hold ETH to pay gas fees, Stablechain uses USDT for transaction costs. This simplifies the user experience and aligns fees with the stablecoin’s value, making it ideal for remittances and micropayments. Peer-to-peer USDT transfers are gas-free, a feature that could disrupt traditional payment models.
Ultra-Low Fees and Instant Settlement: The blockchain claims to confirm transactions within seconds with fees below a fraction of a cent. This is a significant improvement over networks like Ethereum, where ERC-20 USDT transfers can cost several dollars during peak times, as noted in gas fee analyses from 2022.
High Throughput: Stablechain is engineered to handle thousands of transactions per second, a capability rooted in its StableBFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance) consensus mechanism. This high throughput draws inspiration from research on scalable consensus algorithms, such as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)-based systems, which enhance transaction processing without sacrificing security.
Enterprise-Grade Security and Scalability: Institutions gain guaranteed blockspace allocation and batch processing, addressing the needs of high-volume users. The platform also promises robust security measures, though specifics remain under wraps.
Cross-Chain Interoperability: Using USDT0 and LayerZero technology, Stablechain enables seamless bridging to other ecosystems, enhancing its utility in a multi-chain world.
Developer-Friendly Ecosystem: With full EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatibility, specialized SDKs, and APIs, developers can build stablecoin-centric decentralized applications (dApps), from payment platforms to lending protocols.
Stable Wallet: This user-friendly interface includes social login, card integration, and human-readable aliases, lowering the barrier to entry for non-technical users.
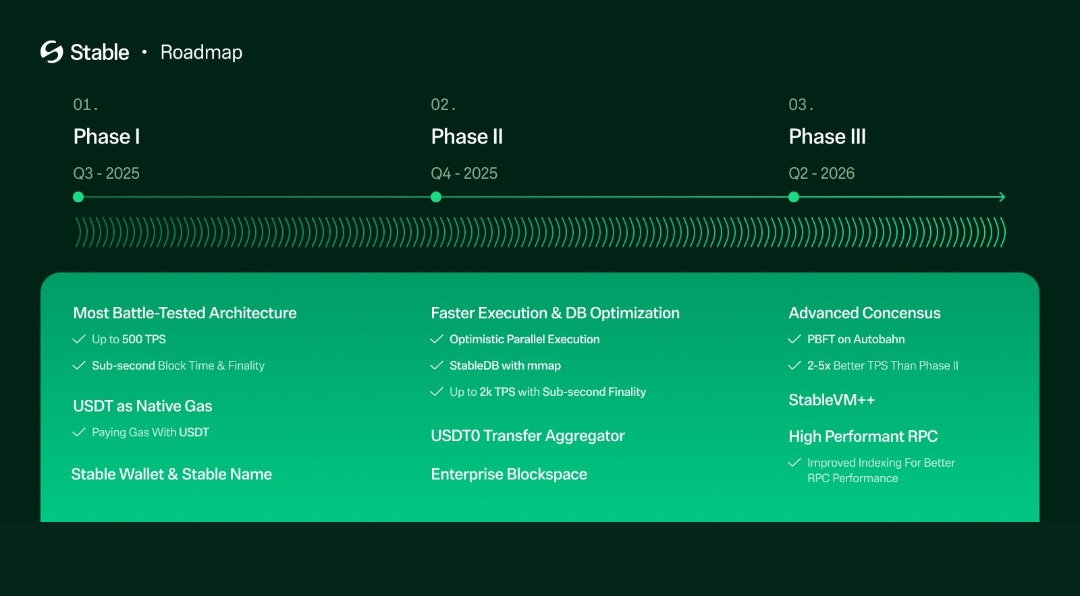
The Roadmap: A Vision for the Future
Stablechain’s multi-phase roadmap outlines an ambitious evolution:
- Phase 1 (Current): Focuses on USDT as the native gas token, StableBFT for sub-second finality, and the launch of the Stable Wallet.
- Phase 2: Introduces optimistic parallel execution and USDT transfer aggregators to boost throughput, alongside dedicated blockspace for enterprises.
- Phase 3: Upgrades to a DAG-based consensus for enhanced speed and resilience, expanding developer tools for broader dApp development.
This progression reflects insights from academic literature, such as IEEE studies on DAG-based consensus algorithms, which prioritize scalability and efficiency—key for a stablecoin-optimized chain.
Implications and Challenges
Stablechain’s potential is vast. For individuals, gas-free global transfers could rival services like Wise or PayPal. Enterprises could bypass costly third-party processors, reducing transaction expenses significantly. Developers gain a sandbox to innovate with stablecoin-based solutions, potentially accelerating DeFi growth. The integration of USDT, which already handles massive transaction volumes, positions Stablechain as a contender to reshape the digital economy.
However, the project faces scrutiny. A user on X, @vinibarbosabr, highlighted a critical gap: the lack of transparency around the consensus mechanism and validator identity. Without clear details on who validates transactions, Stablechain risks being perceived as a centralized database rather than a true decentralized Layer 1 blockchain. Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) mechanisms, as outlined in resources like Nervos.org, require a distributed network of nodes to agree on transactions, ensuring security even against malicious actors. If Stablechain relies on a limited set of validators—potentially controlled by Tether or its partners—it could undermine its decentralization claims, a cornerstone of blockchain trust.
Moreover, the use of USDT as a gas token ties Stablechain’s success to Tether’s stability and regulatory standing. With ongoing debates about USDT’s reserves and centralization, any instability could ripple through the ecosystem. The absence of data on validator distribution or consensus specifics, as of 02:40 AM WAT on July 2, 2025, fuels speculation about whether Stablechain is a groundbreaking innovation or a centralized solution in disguise.
The Bigger Picture
Stablechain reflects a broader trend in blockchain development: specialization. Just as Ethereum caters to smart contracts and Solana prioritizes speed, Stablechain carves a niche for stablecoins. Its emphasis on low-latency, high-throughput transactions aligns with the growing demand for real-time financial systems, a theme echoed in peer-reviewed analyses of blockchain consensus evolution (e.g., Springer’s Cybersecurity journal). Yet, its reliance on USDT and lack of validator transparency invite comparisons to centralized payment networks, challenging the ethos of decentralizatio
Stablechain represents a bold experiment in blockchain design, leveraging USDT’s dominance to create a stablecoin-optimized ecosystem. Its technical innovations—USDT gas, instant settlements, and high throughput—address real pain points, offering a glimpse into a future where digital payments are as seamless as texting. However, its success hinges on resolving transparency issues around its consensus mechanism and validator network. As the project unfolds, the crypto community will watch closely to see if Stablechain delivers on its promise to unlock the full potential of stablecoins or if it stumbles under the weight of centralization concerns.
For those intrigued, the Stable website (https://stable.xyz) and technical documentation provide a starting point to explore further. Whether Stablechain becomes the backbone of a new financial era or a cautionary tale remains to be seen—but its launch marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing evolution of blockchain technology.